A Case Report of an Atypical Presentation of Fournier’s Gangrene
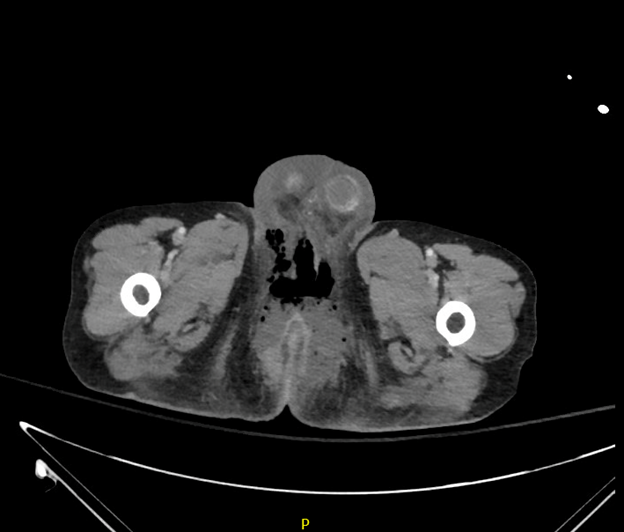
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis was significant for scrotal fluid and punctate gas locules (red arrow) without discrete evidence of invasion into the adjacent soft tissues, suspicious for Fournier’s gangrene. There was also fluid collection centered around the seminal vesicles suggestive of an abscess.